This is a look at an ADSL Device, specifically using the example of the model and make of a Dynalink RTA Modem/Router.
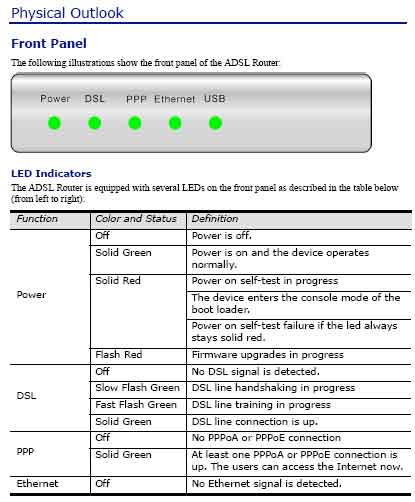
An ADSL Device allows us to use frequencies on our phoneline that we cannot hear through the telephone itself. These frequencies allow data to travel at high speeds. Following is a graphical example of the front panel on an ADSL device.
Notice the various types of statuses per light, the example below shows them as if they were all solid green.
rta1320_p1_frontpanel

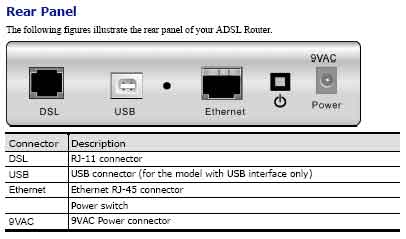
Following is a graphical look at the
back of the ADSL device. Notice the different ports at the back. A description
of them follows.
rta1320_p2_rearpanel
To access the ADSL Router via Ethernet, the host computer must meet the following requirements:
The ADSL Router is configured with the default IP address of 192.168.1.1 and subnet
mask of 255.255.255.0. As the DHCP server is Enable by default, The DHCP clients should be able to access the ADSL Router. Or you could assign an IP address to the host PC first for initial configuration.
You also can manage the ADSL Router through a web browser-based manager: ADSL ROUTER CONTROL PANEL. The ADSL Router manager uses the HTTP protocol via a web browser to allow you to set up and manage the device.
To configure the device via web browser, at least one properly-configured PC must
be connected to the network (either connected directly or through an external
hub/switch to the LAN port of the device).